|
Standards for Play Therapy, Therapeutic Play and Filial Play
PTISA has adopted the PTI standards.
PTI has, always led the way, since 1985, in setting standards to ensure high quality of care when play therapy, therapeutic play skills and filial play are used with children to improve emotional literacy and alleviate behaviour and mental health problems. There have been major revisions in 2001, with the adoption of PTUK’s Ethical System and Competency Framework and in 2006 with additions to the Competency Framework, the inclusion of Filial Play and the application of a four stage model of evaluation based on Kirkpatrick principles. (‘Play for Life’ journal Autumn/Winter 2006 edition).
The three main areas of standards are:
|
An Ethical System
|
To protect the children, their carers and the practitioners.
|
|
Profession Structure Model
|
To provide a coherent structure for the development of the profession including education
and training standards based on a competency framework.
|
Clinical Governance
|
To manage the quality of therapeutic work and continuing professional development. The Play Therapy Dimensions Model, introduced in 2005 is a recommended therapy decision taking method.
|
PTI standards, are continually reviewed, based upon the needs of clients - the children, those who are responsible for them - parents and carers, referrers - teachers, nurses, social workers, doctors etc and those that commission therapeutic services. The standards are produced through a collaborative process involving consultation with international members of the profession. All standards are kept under constant review by PTI's Executive and Advisory Boards.
The context of play therapy standards is shown in PTI’s Play Therapy Practice Systemic View diagram. This is the basis of PTI’s approach to standards providing an overall architecture. It guards against a piecemeal approach being taken.
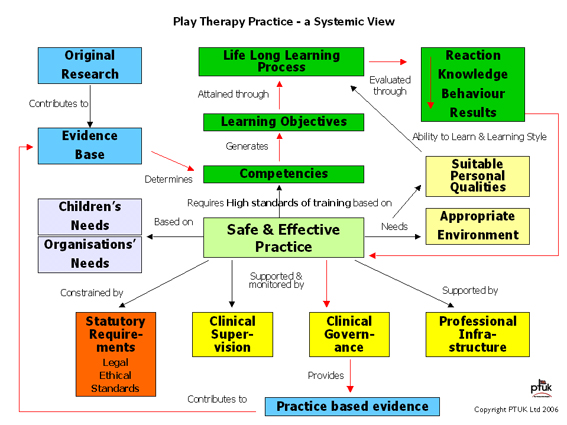
Safe and effective practice requires high standards of training based on competencies from which learning objectives are derived. The learning objectives are attained through a life-long learning process. The effectiveness of the learning process is evaluated at four levels: reaction, learning, behaviour and results.
Safe and effective practice also requires an appropriate environment for practice and the practitioner needs to have suitable personal qualities. More Here.
Safe and effective practice must be based on the needs of the children, the parent/carers and the commissioning organisation or agency. It is constrained by statutory requirements and legal and ethical considerations.
The practitioner is supported and monitored by clinical supervision, a professional infrastructure (provided by PTI) and clinical governance. Clinical governance provides practice based evidence to the evidence base which is also fed by original research. The evidence base contributes to the development and refinement of competencies.
For brief introductions
Providing a good standard of practice and care
Ethical System
Profession Structure Model
Clinical Governance
Providing a good standard of practice and care
All clients are entitled to good standards of practice and care from their practitioners in play therapy, filial play , child psychotherapy and counselling. Good standards of practice and care require professional competence (see the Profession Structure Model); good relationships with clients and colleagues; clinical supervision; commitment to and observance of professional ethics and the use of clinical governance procedures.
Ethical System
All PTI Practitioner Members are required to work within the PTI Ethical System (link to EthicalFramework1) or an equivalent.
Profession Structure Model
The second version of this model was released in June 2003. It contains a competency framework which can be used to:
Increase the understanding of the work of therapists in detail - what do they do precisely? Does this meet the organisation's or individual's needs?
Form the basis of identifying training needs - what skills do therapists need to acquire?
Provide a basis to produce job descriptions - what should a therapist be expected to do?
Enable performance appraisals to be based on observable behaviours as well as results
PTUK Practitioner Members are advised to use, the Model for career development planning.
Employers are recommended to apply the principles to all therapeutic work with children.
Clinical Governance
Clinical Governance is a health profession term for quality management.
Clinical governance is based upon collecting quantifiable measurements (normally pre and post therapy outcomes), carefully analysing the data to detect both good and poor results and using the conclusions to improve practice.
Clinical governance is sometimes referred to as practice based evidence, which is equally, if not more important, than evidence based practice.
All PTI Practitioner Members are strongly advised to use an approved method of clinical governance. It is mandatory for PTI Trainees.
|